what is the resultant velocity|what is a resultant vector : Cebu Velocity: The velocity of an object is how fast it is moving in a particular direction. It is a vector. The SI unit for velocity is meters per second, m s . We will use all these steps and. Convert 100 KWD to PHP with the Wise Currency Converter. Analyze historical currency charts or live Kuwaiti dinar / Philippine peso rates and get free rate alerts directly to your email.
PH0 · what is a resultant vector
PH1 · what does negative velocity mean
PH2 · definition of velocity in physics
PH3 · Iba pa
48,427 Free images of Eyes. Free eyes images to use in your next project. Browse amazing images uploaded by the Pixabay community. Royalty-free images. eye close up vision. Edit image. . Over 5 million+ high quality stock images, videos and music shared by our talented community.
what is the resultant velocity*******The resultant velocity of an object is the sum of its individual vector velocities. . The sum of the vector forces on an object is equal to the scalar product of the object's mass and its acceleration vector. View chapter Explore book.
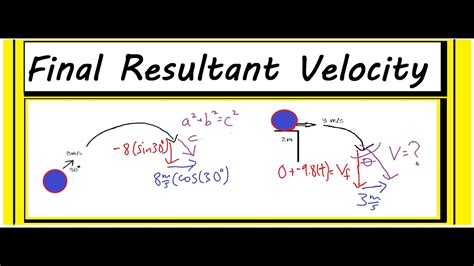
How to Calculate Resultant Velocity. Part of the series: Physics Education. Calculating resultant velocity can be accomplished through the use of a very spec.
When an object, say, a boat, travels at a certain velocity, and the medium through which it travels, say, a river, has its own velocity, we can find the resultant velocity of the object by . The resultant velocity refers to the overall velocity of an object when multiple velocities are combined. It is the vector sum of all the individual velocities. When .Velocity: The velocity of an object is how fast it is moving in a particular direction. It is a vector. The SI unit for velocity is meters per second, m s . We will use all these steps and. Using the velocity addition rule, the relative motion equation we are seeking is \[\vec{v}_{CT} = \vec{v}_{CE} + \vec{v}_{ET} \ldotp \label{ex2}\] Here, \(\vec{v}_{CT}\) . IN THIS VIDEO WE LOOK AT RESULTANT VELOCITY. WHAT IS RESULTANT VELOCITY AND HOW TO CALCULATE RESULTANT VELOCITY FOR QUESTIONS CONCERNING VELOCITY . Keep going! Check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning:https://www.khanacademy.org/math/precalculus/x9e81a4f98389efdf:vectors/x9e81a4f98389e.

At its core, the Resultant Velocity Calculator is designed to compute the final velocity of an object when it undergoes acceleration over a certain period. This . At its core, the Resultant Velocity Calculator is designed to compute the final velocity of an object when it undergoes acceleration over a certain period. This .
What would be the resultant velocity of the motorboat (i.e., the velocity relative to an observer on the shore)? The magnitude of the resultant can be found as follows: (4.0 m/s) 2 + (3.0 m/s) 2 = R 2 What is resultant velocity examples? Multiply the acceleration by the time the object is being accelerated. For example, if an object falls for 3 seconds, multiply 3 by 9.8 meters per second squared, which is the acceleration from gravity. The resultant velocity in this case is 29.4 meters per second.The resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the result will be vector R. As shown in the diagram, vector R can be determined by the use of an accurately drawn, scaled, vector addition diagram. The fundamental equation that powers the Resultant Velocity Calculator is: v_f = v_i + a*t. where: v_f is the final velocity (magnitude and direction), v_i is the initial velocity (magnitude and direction), a is the acceleration (positive for speeding up, negative for slowing down), t is the time in seconds.
Average velocity is defined to be the change in position divided by the time of travel. v a v g = Δ x Δ t = x f − x 0 t f − t 0. In this formula, v a v g is the average velocity; Δ x is the change in position, or displacement; and x f and x 0 are the final and beginning positions at times t f and t 0 , respectively. The vector equation is →vPG = →vPA + →vAG, where P = plane, A = air, and G = ground. From the geometry in Figure 4.6.6, we can solve easily for the magnitude of the velocity of the plane with respect to the ground and the angle of the plane’s heading, θ. Figure 4.6.6: Vector diagram for Equation 4.6.2 showing the vectors →vPA, →vAG .
a plane flying due east at 200 km/h encounters a 40-km/h wind blowing in the north-east direction. the resultant velocity of the plane is the vector sum v = v1 v 1 + v2 v 2, where v1 v 1 is the velocity vector of the plane and v2 v 2 is the velocity vector of the wind. the angle between v1 v 1 and v2 v 2 is pi/4. determine the resultant speed .what is the resultant velocityQuestion Video: Calculating the Resultant Velocity after Accelerating. An aircraft is flying eastward, accelerating at 12 m/s². The aircraft is also descending vertically with an acceleration of 9 m/s². Before accelerating, the eastward velocity of the aircraft was 250 m/s and its vertical speed was 10 m/s.
what is a resultant vector The resultant velocity of an object is the sum of its individual vector velocities. The sum of the vector forces on an object is equal to the scalar product of the object’s mass and its acceleration vector. What is resultant moment? In this video, the concept of how to combine the correct velocity vectors is discussed. Two examples are worked out to show how to solve for the correct hor.The velocity of the plane = V a = 100 km/hr. The relative velocity of the plane with respect to the ground can be given as. The angle between the velocity of the wind and that of the plane is 90°. Using the Pythagorean theorem, the resultant velocity can be calculated as, R 2 = (100 km/hr) 2 + (25 km/hr) 2. R 2 = 10 000 km 2 /hr 2 + 625 km 2 .The Resultant velocity for two velocity components is known from kinematics flow while considering the velocity components u and v in the relation between stream function and velocity potential function is calculated using Resultant Velocity = sqrt((Velocity Component at U^2)+(Velocity Component at V^2)).To calculate Resultant velocity for .Before proceeding to the next step, lets determine “the velocity of the water relative to the freighter”, V. wf. The following is a unique feature of case 2 relative velocity problems. That is V. wf. = - Vfw. This means the size of both velocities are the same, but the directions of each are perfectly opposing.what is the resultant velocity what is a resultant vector in this video we look at resultant velocity. what is resultant velocity and how to calculate resultant velocity for questions concerning velocity that is act.The resultant velocity is simply the vector sum of these two velocities. The first step to answering this question involves sketching a vector addition diagram in which you add the boat velocity and the river velocity head-to-tail. The resultant velocity will this stretch from the tail of the boat velocity (if drawn first) to the arrowhead of . The resultant velocity of an object is the sum of its individual vector velocities. The sum of the vector forces on an object is equal to the scalar product of the object’s mass and its acceleration vector. What is another word for resultant? In this page you can discover 31 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for .
A motorboat is moving towards north at 25 km/hr and rate of flow of water is 10 km/hr along a direction of 60 degrees east of south. Find the resultant velocity of the boat and the direction in which; A rowboat is heading across a river at 2.4 m/s east. The current of the river is 1.7 m/s south. What is the rowboat's resultant velocity? What is the formula of resultant velocity? Velocity Formula Add this velocity to the initial velocity. In the example above, if the object had an initial velocity of 5 meters per second, the resultant velocity would be 34.4 meters per second. The overall formula here is v (final) - at + v (initial) where "v" is velocity, "a" is acceleration and . Resultant velocity would be the velocity of an object (in some fixed reference frame) when there are more than one influences on its motion. What is a resultant velocity? The resultant velocity of an object is the sum of its individual vector velocities. The sum of the vector forces on an object is equal to the scalar product of the object’s .
Your Metro Manila Commuting Guide. Public Transport Directions: Jeepneys, Trains, Buses, P2P, UV Express, Pasig River Ferry, Libreng Sakay, and more!
what is the resultant velocity|what is a resultant vector